

WHO classification and criteria for the myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS)
Refractory Anemia (RA)
Peripheral Blood
Anemia
No or rare blasts
Bone Marrow
Erythroid dysplasia only
<5 percent blasts
<15 percent ringed sideroblasts
Refractory Anemia with Ringed Sideroblasts (RARS)
Peripheral Blood
Anemia
No blasts
Bone Marrow
Erythroid dysplasia only
<5 percent blasts

Refractory Cytopenia with Multilineage Dysplasia (RCMD)
Peripheral Blood
Bi- or pan-cytopenia
No or rare blasts
No Auer rods
Monocytes <1,000/µL
Bone Marrow

No Auer rods
<5 percent blasts
<15 percent ringed sideroblasts
Refractory Cytopenia with Multilineage Dysplasia and Ringed Sideroblasts (RCMD-RS)
Peripheral Blood
Bi- or pan-cytopenia
No or rare blasts
No Auer rods
Monocytes <1,000/µL
Bone Marrow
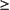
No Auer rods
<5 percent blasts
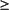
Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts-1 (RAEB-1)
Peripheral Blood
Cytopenias
<5% blasts
No Auer rods
Monocytes <1,000/µL
Bone Marrow
Unilineage or multilineage dysplasia
5-9 percent blasts
No Auer rods
Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts-2 (RAEB-2)
Peripheral Blood
Cytopenias
5-19% blasts
Auer rods ±
Monocytes <1,000/µL
Bone Marrow
Unilineage or multilineage dysplasia
10-19 percent blasts
Auer rods ±
MDS-Unclassified (MDS-U)
Peripheral Blood
Cytopenias
No or rare blasts
No Auer rods
Bone Marrow
Unilineage dysplasia in granulocytes or megakaryocytes
No Auer rods
<5 percent blasts
MDS with del(5q) "5q- syndrome"
Peripheral Blood
Anemia
<5 percent blasts
Platelets usually normal or increased
Bone Marrow
Normal to increased megakaryocytes with hypolobulated nuclei
No Auer rods
<5 percent blasts Isolated del(5q)
Note: In this proposed WHO system, the FAB MDS subgroup Refractory Anemia with Excess Blasts in Transformation (RAEB-T) has been taken out of the MDS classification and is now considered Acute Myeloid
Leukemia with Multilineage Dysplasia.
Adapted from Brunning, RD, et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes: Introduction. In: Jaffe, ES, Harris, NL, Stein, H, Vardiman, JW, editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC Press: Lyon 2001, p. 63. Permission granted from Harris, NL and Vardiman, JW.
Subtype incidence — Partitioning of 1640 cases taken from the available literature according to the original FAB classification system was:
•Refractory anemia — 21 percent
•Refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts — 17 percent
•Refractory anemia with excess blasts — 37 percent
•Refractory anemia with excess blasts in transformation — 12 percent
•Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia — 13 percent
I. Classification

Calculator: Myelodysplastic Syndrome International Prognostic Scoring System
Percentage of Bone Marrow Blasts
< 5 percent (0 points)
5 to 10 percent (0.5 points)
11 to 20 percent (1.5 points)
21 to 30 percent (2.0 points)
Karyotype
Normal, Y-, 5q-, 20q- (0 points)
Abnormal chromosome 7 or 3 or more abnormalities (1.0 points)
All other cytogenic abnormalities (0.5 points)
Cytopenias
(defined as hemoglobin < 10 g/dL, absolute neutrophil count < 1800/microL, platelet count < 100,000/microL)
No cytopenia or cytopenia of 1 cell type (0 points)
Cytopenia of 2 or 3 cell types (0.5 points)
Total Criteria Point Count:
Prognostic Score Interpretation
0 Points : Low (Median Survival of 5.7 yrs) 0.5 - 1 Points : Intermediate 1 (Median Survival of 3.5 yrs.) 1.5 - 2.0 Points : Intermediate 2 (Median Survival of 1.2 yrs.) 2.5-3.5 Points : High (Median Survival of 0.4 yrs.)


Median survival (in years) in myelodysplastic syndrome according to IPSS and age

Low 11.8 4.8 3.9
Intermediate-1 5.2 2.7 2.4
Intermediate-2 1.8 1.1 1.2
High 0.3 0.5 0.4
Adapted from Greenberg, P, Cox, C, Le Beau, MM, et al, Blood 1997; 89:2079.



EPO use Guidelines – Oct 2009
For Chemotherapy Induced Anemia
I. Recommended to obtain lab work each time drug is administered for reimbursement.
II. Medicare Guidelines – ESAs are not indicated for patients receiving myelosuppressive therapy when the anticipated outcome is cure.
-
III.For chemotherapy and radiation induced anemia: Hgb must be less than 10.0 or Hct less than 30.0.
ICD-9 Codes for Chemotherapy induced anemia (3 code combo):
285.9 Anemia
995.20 Adverse Effect medicinal substance
E933.1 Antineoplastic and/or immunosuppressive drugs
IV. Maximum dose 50,000 units weekly.
And for radiotherapy-induced anemia
Hgb must be less than 10.0 or Hct less than 30.0.
ICD-9 Codes for Radio-induced anemia (2 code combo):
285.9 Anemia
E879.2 Adverse effect radiation
IV. Also maximum dose is 50,000 units weekly.
For non-chemotherapy or radiation induced anemia
For documentation of Myeodysplastic S. and Anemia requiring treatment it is needed to document 2 codes, one for MDS and one for anemia.
Example:
Assessment and Plan
-
1.Myelodysplastic Syndrome (238.72)
-
2.Anemia (285.9) due to Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Proceed with Procrit treatment and instruction as specified on Procrit order sheet.
Codes for use with
-
1.Chronic Renal Insufficiency (2 code combo):
285.21 Anemia in chronic kidney disease AND
585.9 Renal insufficiency
-
2. Myelodysplasia (2 code combo):
238.72 Myelodysplastic Syndrome (low grade) OR
238.73 MDS High Grade, OR
238.74 MDS with 5q deletion, OR
238.75 MDS unspecified, AND
285.9 Anemia
-
3.Hepatitis C (2 code combo):
285.29 Anemia of Chronic Disease AND
070.70 Hepatitis C
-
4.HIV (2 code combo):
285.29 Anemia of Chronic Disease AND
V08 HIV status asymptomatic
-
5.Rheumatoid Arthritis ( 2 code combo):
285.29 Anemia of Chronic Disease AND
714.0 Rheumatoid Arthritis
-
6.Pre-surgical
V72.85 Spec Pre-Operative Exam AND
285.9 Anemia, unspecified.
-
-
-
I. Initial pretreatment Hgb must be less than 10.0 or Hct less than 30.0
II. To continue ESA, Hgb must be less than 11.0 or Hct less than 36.0.
III. Notice that maximum dose is 90,000 units weekly.
Helps with EPO Dictation
Most always dictate Anemia alone, as a diagnosis (and code) when using EPO.
Always put diagnosis that we need for coding in ending of dictation (assessment and plan section).
Be definitive, don’t say “may be due to”, “seems to be”.
If Macrocytic Anemia is dictated, EPO will not be covered.
If iron deficiency is dictated, EPO will not be covered.
If B12 deficiency is dictated, EPO will not be covered
Sideroblastic Anemia is not covered, Sideroblastic Anemia, Refractory is covered as MDS low grade.
